Composable Data Management System
2022 年 VLDB 新组织了一个 Workshop,叫做 International Workshop on Composable Data Management Systems (CDMS)。CDMS 的目标是让数据库学术界、工业界和用户等一起 来探讨如何通过可组合性和可复用性来设计数据库系统。第一期的议程1包括:
-
Keynotes
例如 Microsoft 的 From parsing, to query processing, to resiliency: Deriving unexpected value from database technology through componentization, Intel 的 Evolving an Organization’s Data Management Discipline in support of their Machine Learning Activities, 开源社区的 Substrait: Rethinking DBMS Composability2, Jacques Nadeau, 以及 DuckDB - A Modern Modular & Extensible Database System。
-
Invited talks
例如:SAP’s global data mesh for composable data management supporting cross-domain consumption,GoogleSQL: A SQL Language as a Component,Snowflake 的 The Single Product Approach: Supporting Diverse Workloads with Snowflake’s Query Engine,Deltalake 的 Delta Lake: The one storage format for all your analytics,Facebook 的 Velox: Unifying execution engines across Meta and beyond。
-
Short papers
Discussion
CDMS 2022 中有一篇论文为:https://www.firebolt.io/content/firebolt-vldb-cdms-2022 , 它是个非常典型的拿来主义式设计,基于现有的各种开源组件打造一个产品。软件工程领域 把这个叫做:Opportunistic Design 5, 6,翻译成中文应该叫机会主义式设计。 引用一段 Programming the Tip of the Iceberg: Software Reuse in the 21st Century 6 的原文如下:
Opportunistic design - An approach in which people develop new software systems
by routinely reusing and combining components that were not designed to be used
together - has recently become very popular. This emergent pattern places focus
on large scale reuse and developer convenience, with the developers "trawling"
for most suitable open source components and modules online.
This approach is all about combining unrelated, often previously unknown
hardware and software artifacts by joining them with “duct tape and glue code”
[8]. Depending on one's viewpoint and desired connotation, such development is
referred to as opportunistic design [8], opportunistic reuse, ad hoc reuse,
scavenging [9], mashware [10], [11], or sometimes even “frankensteining”
[8]. The resulting approach bears the imprint of cargo-cult programming [12] -
the ritual inclusion of code or program structures for reasons that the
programmers do not fully understand.
上面引用的论文所描述的设计方式在最近 20 年确实特别普遍,尤其是像 Java、Python 等 提供了大量优秀第三方库的语言生态里头更是如此。显然,CDMS 的愿景比这要高出几个 Level,期望做系统底层或组件的组织能够从一开始就为数据管理系统的模块复用打好基础。 如果回顾历史,在开源软件还没有大行其道的年代,业界的领袖厂商是通过标准化机制来争 夺和促进软件标准化和互操作的。典型的例如通信领域的 IETF(RFC)、数据库领域的 ISO/IEC(SQL)等标准组织。只不过大量涉及内部模块实现的地方都很难标准化,没有哪个 大厂商愿意失去对核心技术的控制、确保技术演进自主性以及将用户 Locked-in 的诱惑。 例如,数据库标准化组织其实也试过将客户端与服务器的通讯协议标准化,最终还是失败了。 而开源数据库则通过开源和生态建设,形成了多种多样的事实标准:MySQL、PostgreSQL 等 都用的是不同的通讯协议。
在开源社区和学术界进行数据管理软件底层组件的可组合、可复用也许是一种可行的思路。 不过这需要在系统的设计和迭代过程中进行长期的磨合,既要求整个系统的设计,例如像 DuckDB 那样充分考虑到组件化、可拔插、可扩展,也要求组件的设计。又例如像 Arrow 等 具备足够的通用性和适应性。简单的把各种部件组合在一起的系统,要不无法工作,要不就 是效率太差而没有什么竞争力。从经典的 SQL 处理流程来看,包括 Wire protocol、SQL Statemnt、AST、逻辑计划、物理计划、执行器等,每一层都最好要做成可以被旁路接入的, 很明显这里的难度非常大。毕竟能把优化器或执行器整个做成可拔插的系统也还没有几个, Calcite 已经算是非常成功的项目了。另外一个工程上的挑战是如何做到跨语言的组件高效 地互通互联,例如 C/C++ 写的组件与 Java 写的组件的交互。Substrait 2 , 7 的目标是做一个跨平台/跨语言的关系代数或查询计划表达,也已经在开源的 OLAP 领域有 一些对接和实践了,也许未来的几年就会看到它的尝试结果。
从上面的讨论可以看出,Composable Data System 最主要的领域还是 OLAP,而不是 OLTP。 因为前者在传统数据库、数据仓库以及大数据的发展演化过程中已经形成了较为统一的架构 设计:
- 存算分离,以对象存储作为共性的存储底座。
- 数据格式统一,形成了 Parquet、ORC 等少数几种通用的数据格式。
- 表或 Schema 概念统一,初步形成了 Hudi、Deltalake 等少数几种表的格式。
- 元数据管理统一到 Hive Meta Store 等系统。
- 优化器虽然还没那么统一,但 Calcite 可以算是比较成功。
剩下的主要还是在语言和 API 生态、以及功能侧重点上的竞争。那么,不久的将来,此类 产品的竞争力到底在哪里呢?也许是易用性,也许是整合整个 Data Pipeline 的生产效率 的提高?还是说我们大部分做系统的人都要堕落成为类似于手机壳或 QQ 皮肤的生产者? 或者,包云岗老师说的道理也能用到 CDMS:
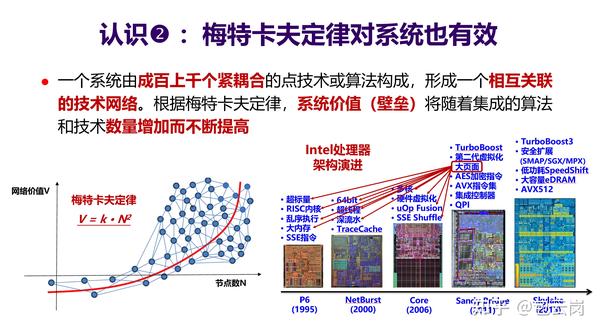
根据梅特卡夫定律,当一个网络内的节点数越多,那么整个网络的价值也就越大。因此,
通过不断积累,让一个系统集成越来越多的点技术,那么该系统的价值就会越来越大。
当然,网络越复杂,集成的难度也就越大。但是,一旦通过技术攻关成功实现新算法或
新功能的集成,构成一个更大的技术网络,那么壁垒也就更高。
作者:包云岗
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/619712830
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
Related Work
从 CDMS 的参会者和会议内容可以看出,主要的工业界力量来自开源社区:DuckDB,著名的 开源单机 OLAP 数据库;Substrait、Velox、Delta Lake、Filebolt,来自大数据/数据湖 领域。学术界的 Vision 则显得更高深莫测(或不切实际)一些,在 CIDR 等会议上往往有更 激进的架构性设计。例如:AnyDB - An Architecture-less DBMS for AnyWorkload 8, DBOS - A Database-Oriented Operating System 9。Berkeley 搞了有几年的 Ray10 显得更成熟一点,不过它的目标是: A Distributed System for AI。
Footnotes
1 CDMS Schedule, https://cdmsworkshop.github.io/2022/schedule.html
2 Substrait: Rethinking DBMS Composability, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YXnoBUQP258
3 CDMS Short Papers, https://cdmsworkshop.github.io/2022/shortpapers.html
4 CDMS Proceedings, https://cdmsworkshop.github.io/2022/proceedings.html
5 On opportunistic software reuse, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00607-020-00833-6
6 Programming the Tip of the Iceberg: Software Reuse in the 21st Century, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8906782
7 Substrait Github Repository, https://github.com/substrait-io/substrait
8 AnyDB: An Architecture-less DBMS for Any Workload, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2009.02258.pdf
9 A Progress Report on DBOS: A Database-oriented Operating System, https://www.cidrdb.org/cidr2022/papers/p26-li.pdf
10 Ray: A Distributed System for AI, https://bair.berkeley.edu/blog/2018/01/09/ray/